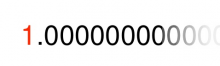Difference between revisions of "Cube constant"
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
One related unit is the cubit (usually denoted "c"), which equals the amount of information in a maxentropic randomness source which has exactly C possible outputs. Equivalently, it is the surprisal corresponding to observing an event with prior probability C. In fact, C is the only constant for which these definitions make any sense. | One related unit is the cubit (usually denoted "c"), which equals the amount of information in a maxentropic randomness source which has exactly C possible outputs. Equivalently, it is the surprisal corresponding to observing an event with prior probability C. In fact, C is the only constant for which these definitions make any sense. | ||
| − | Some useful facts about | + | Some useful facts about the cubit: |
* c = Cc | * c = Cc | ||
Latest revision as of 10:31, 18 June 2023
The Cube constant, often simply written as C, is a very useful number for cubal calculations that pops up all over the place. It is equal to the amount of cube per one cube, and therefore equal to 1[citation needed].
Related units
One related unit is the cubit (usually denoted "c"), which equals the amount of information in a maxentropic randomness source which has exactly C possible outputs. Equivalently, it is the surprisal corresponding to observing an event with prior probability C. In fact, C is the only constant for which these definitions make any sense.
Some useful facts about the cubit:
- c = Cc
- Cc + Cc = c
- Cc = 0c
- 0c ≠ 0°C